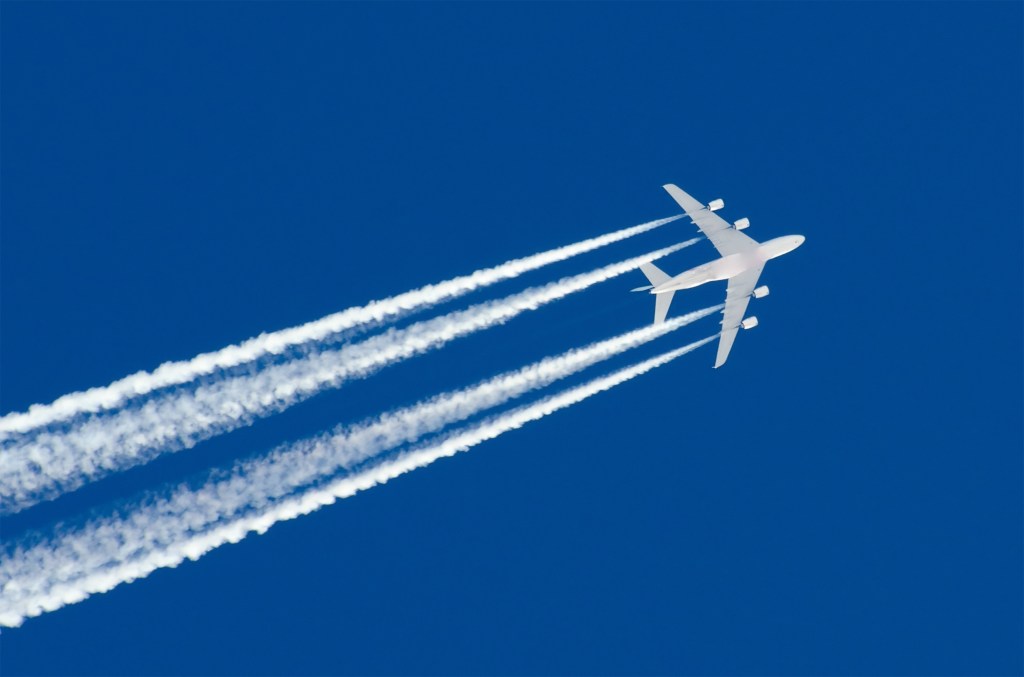

The earliest memory of me seeing a contrail goes way back to my childhood. I was returning from school and was about to enter the main enterance of my house when i saw this huge line of cloud drwan by a small flying object across the sky. I was like “What is that???” I remember i was told it is a rocket going to space. I was happy that i saw a rocket. So, next day i saw another rocket… another one a day after… Every next day somebody is going to space. Day after next I saw two rockets together in the sky travelling in different directions.
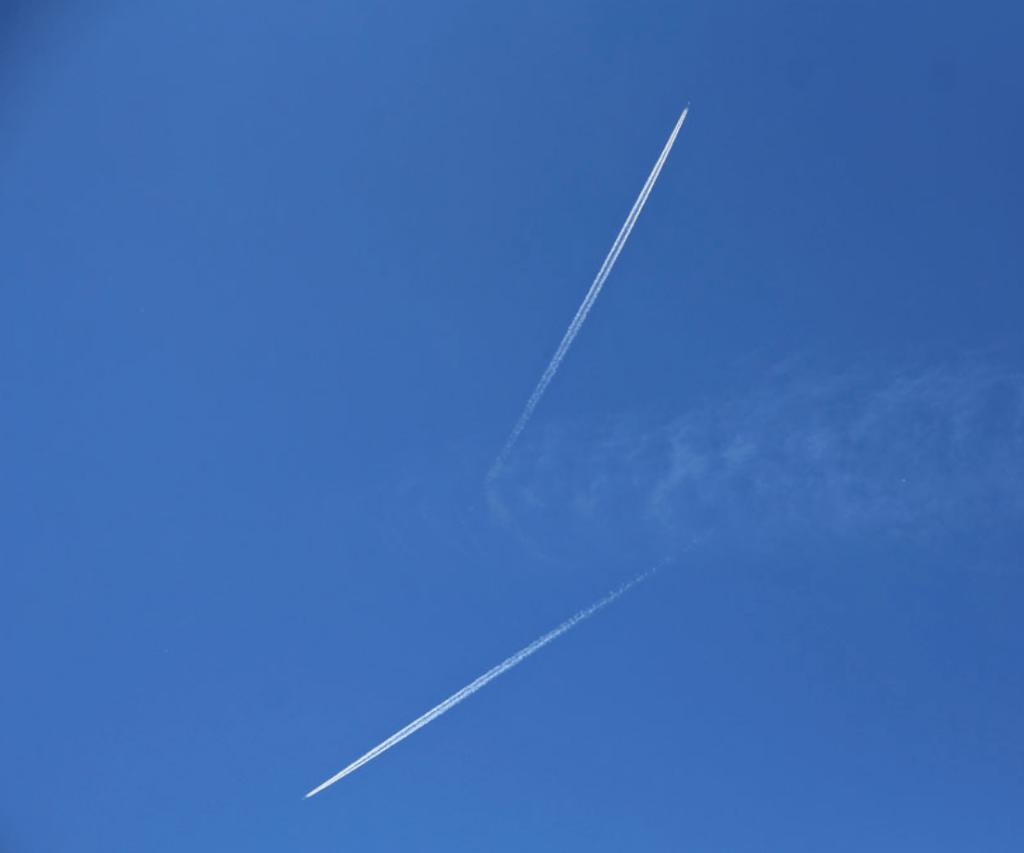

Somebody explained these are the rockets send by two different countries and I accepted…it is funny now, but then, they made me happy.. You know. The feeling of seeing two rockets at a time in thesky of holy city, Varanasi.
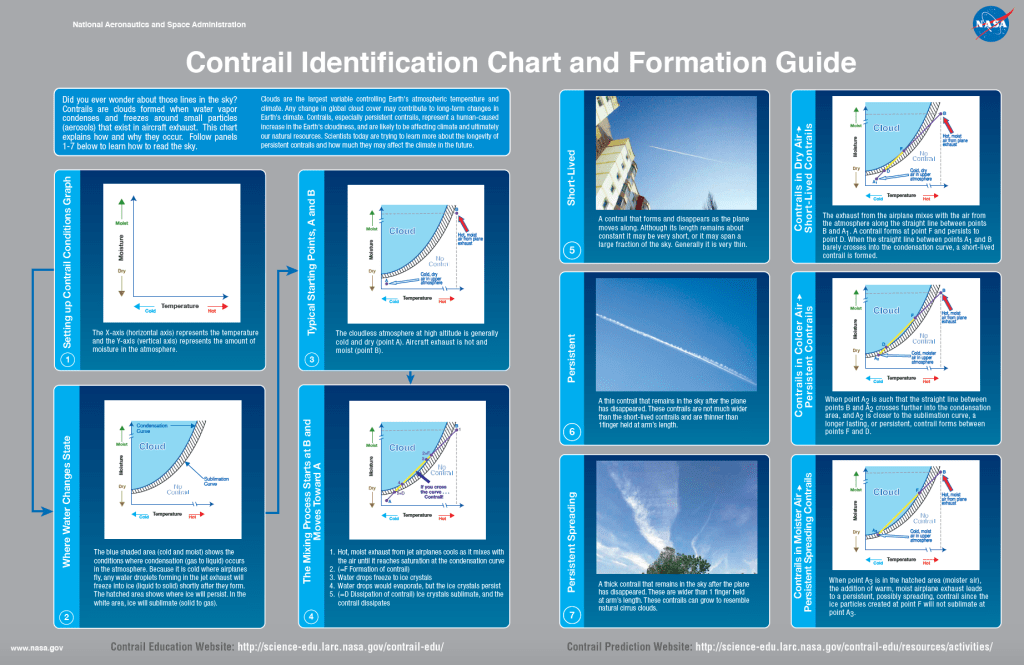
I got curious recently about them. What are they called? How are they formed? Why we dont see it followin every aircraft…and so on. This is when i came to know they are known as contrails. They are the clouds formed when water vapor condenses and freezes around small particles (aerosols) that exist in aircraft exhaust. Some of that water vapor comes from the air around the plane; and, some is added by the exhaust of the aircraft.
The exhaust of an aircraft contains both gas (vapor) and solid particles. Both of these are important in the formation of contrails. These emissions include carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons such as methane, sulfates (SOx), and some metal particles.
There are three types of Contrails:
1. Short Contrails: They look like short white cloud following behind the plane and they disappear almost as fast as the airplane goes across the sky, perhaps lasting only a few minutes or less. This is because the air that the airplane is passing through, is little moist, and there is only a small amount of water vapor available in the surrounding air to form a contrail. The ice particles that do form quickly return again to a vapor state.

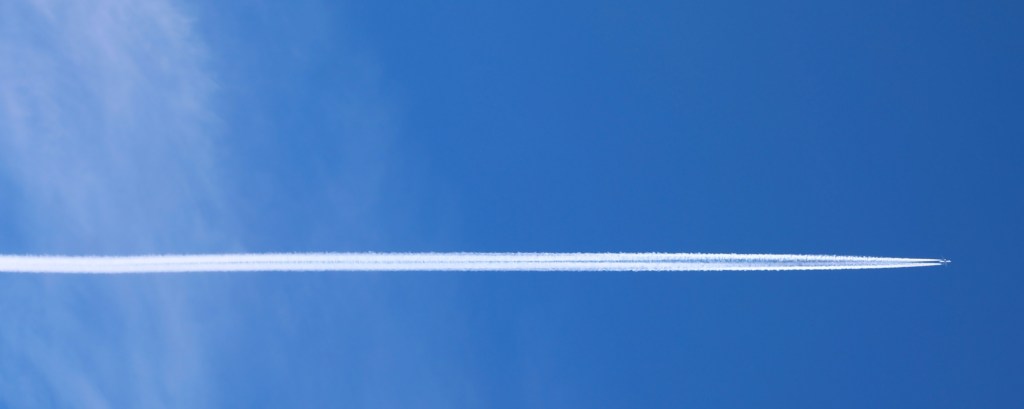
2. Persistent non-spreading contrails: They look like long white line of cloud that remains visible in the sky even after the airplane has disappeared to our eyes. It shows that the air through which the airplane is flying is very humid, and there is a large amount of water vapor available to form a persistent contrail without a strong wind to spread it.

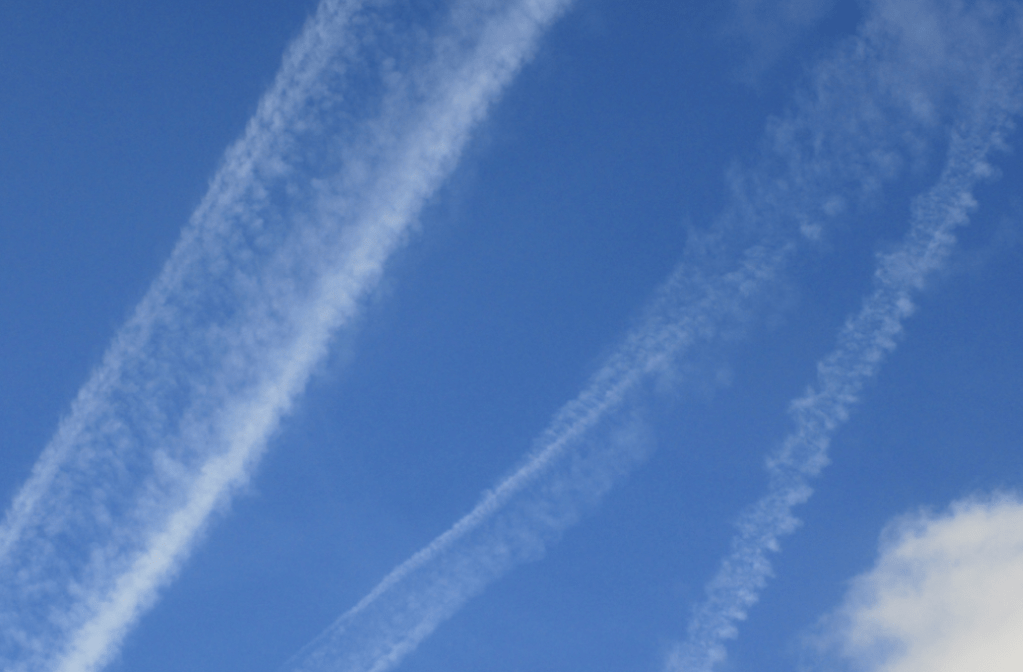
3. Persistent spreading contrail: They are broad, fuzzy white line of cloud. It is formed when the aircraft is passing through air that is very humid acompanied with strong wind. This type of contrails most likely, affects climate because they cover a larger area and last longer than short-lived or persistent contrails.

Why some times we see contrails behind an aircraft where as on some occassions we dont?
There are multiple factors that controls the formation of contrails. If the condition is right thenonly we can see the contrails otherwise we will just see the flight without any contrail.
- If the flying aircraft is flying at lesser altitude the temperature is still not that low so that a contrail can be formed.
- If the humidity is very low the contrails wont form as the ice formed will quickly change its solid state to vapor and we wont see a contrail.
Contrails can move.
As they are formed at very high altitude, they face strong wind., this are strong enough to move the contrail away from the area where they are originally formed. Often we will see old persistent contrails that formed somewhere else but moved overhead because of the wind.
Difference between contrails and cloud.
Contrails are artificial or “human-induced” clouds as they are formed by water vapor condensation and freezing of particles from airplane exhaust. Contrails are always made of ice particles, due to the very cold temperatures at high altitude. Other types of clouds can be formed by water vapor that condenses on particles which are present in the atmosphere due to many sources, such as from volcanoes or dust storms. Those clouds are sometimes made of water droplets, and sometimes ice crystals, depending on the temperature where they form. Contrails only form at very high altitudes (usually above 8 km) where the air is extremely cold (less than -40 degrees C). Other clouds can form at a range of altitudes, from very close to the ground, such as fog, to very high off the ground.



Leave a comment